Rejuvenation / Resurfacing
Laser resurfacing using the carbon dioxide group of lasers is a particularly useful treatment technique for fine wrinkles and is a useful treatment for acne scarring. It is less successful at minimising deep icepick scarring and such pits should generally be excised first (three months before laser resurfacing). The scars which result from such excisions can then be included in the formal resurfacing procedure which follows. It is very unusual to restore acne-scarred skin to normal. The deeper the laser resurfacing is taken, the greater the likelihood of pigmentary changes. This takes the form of either a loss or an increase in the skin's pigmentation, which may be patchy. The risk of pigmentation changes can be minimised by staying out of the sun for at least three months after your treatment and wearing a high-factor sun block at ALL times outdoors. Nevertheless, a worthwhile improvement can often be achieved.
Laser treatment can be performed under a general or local anaesthetic. If you elect to have a local anaesthetic, you can choose to have no sedation, mild sedation (using a tablet under the tongue), or heavy sedation (using an intravenous injection). Local anaesthetic procedures without sedation or with mild sedation can be performed as an Out-Patient. Local anaesthetic procedures with heavy sedation require at least a day case stay. Mild sedation does not require an anaesthetist to be present, whereas heavy sedation does.
Alternatively, you may have laser resurfacing under general anaesthetic either as a day case patient or stay overnight. As a general rule, the greater the area to be resurfaced, the more advisable is a general anaesthetic.
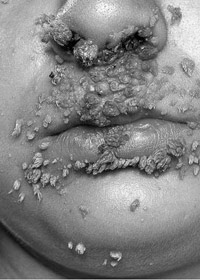
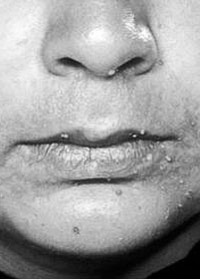
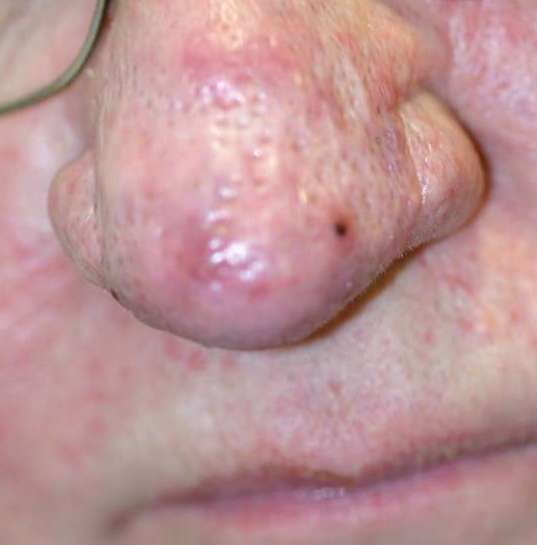
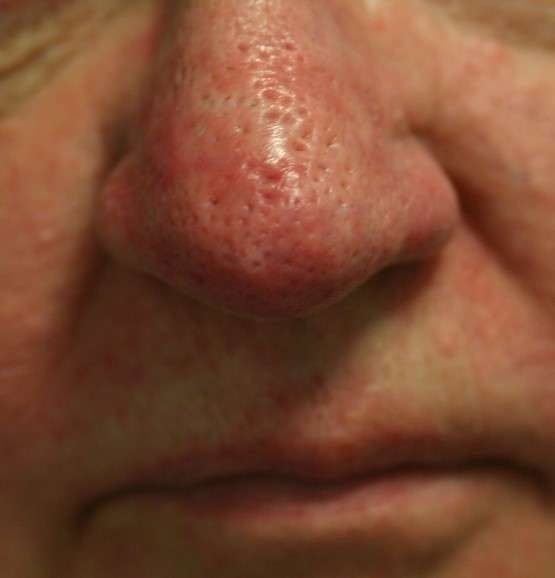
The CO2 laser can also be used to remove certain surface blemishes and pigmentation, or overgrowth of sebaceous tissue for example, in the nose, causing rhinophyma. Because the lesions are literally vaporised, a shave biopsy should first be taken if there is any doubt as to their nature.